OM# Documentation
Conditional: if
ifis a conditional operator, which allows evaluating specific parts of a visual program based on the result of a given test.
The basic syntax (in Lisp) is: (if TEST THEN ELSE)
…where TEST, THEN and ELSE are all expressions returning any type of data.
The condition TEST is said true when it evaluates to anything that is not NIL. Depending on the value of TEST, either THEN (if TEST is non-NIL) or ELSE (id TEST evaluates to NIL) will be evaluated. The result of the chosen expression is returned as the result of the if box.
ELSE is an optional input, and by default, the result of if on a false condition (if TEST evaluates to NIL) is also NIL.
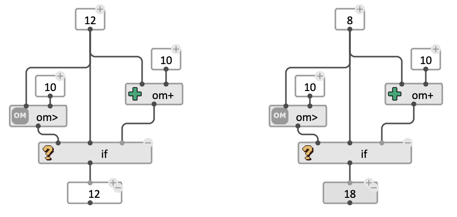
Note: Contrary to most OM# boxes, and Lisp functions,
iffirst evaluates its first input (TEST) in order to determine which one of THEN or ELSE to evaluate next. Therefore, only one of THEN or ELSE input is evaluated.
See also: Logical Operators