OM# Documentation
MIDI Settings
OM# sends and receives MIDI through virtual ports, identified by numbers. The MIDI port is an internal setting found in all the functions and data structures involved with communicating MIDI (e.g. MIDI notes). It can generally be left to NIL, and fallback to the default port.
Score objects and other “MIDI” objects will not sound util their target MIDI port is connected to a MIDI synthesizer or device. → You need to have a MIDI synthesizer or device running or connected to your system, and set the MIDI connections accordingly, from the “MIDI” tab of OM# preferences.
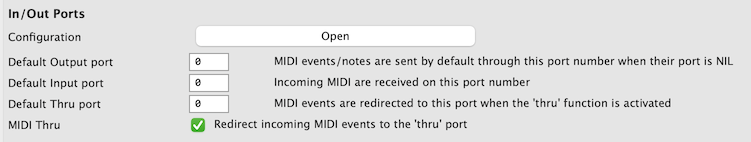
Connecting ports to MIDI devices
The “Configuration” button will allow you to set the routing of OM# MIDI port numbers to the external MIDI devices and synthesizers detected on your computer.
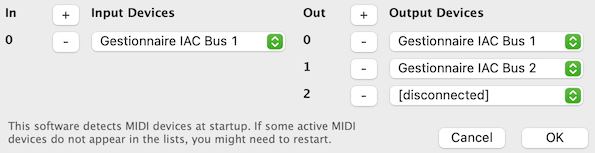
Add in/out ports using the + button (remove them with the - buttons).
Output ports are for playing MIDI (sending events). Input ports are fore receiving and recording MIDI (e.g. from a keyboard, device, or another application).
For each port, a menu allows you to select any connected device or syhthesizer. In the device lists you will see all detected MIDI synths or buses.
Important note: OM# detects MIDI devices at startup; therefore it is possible that a synthesizer started after OM# be not in the list of available MIDI devices. The contents of these menus depends the devices and synthesizers running and connected when you started OM#: You need to restart OM if you connect or start another synth or device that you want to use.
→ See note below about virtual buses, and other platform-spefcific hints.
Default port
Whenever NIL is left as port value, or when there is no option to set the port value, the default input or output ports set in the Preferences will be used.
MIDI “Thru”
MIDI “Thru” is an option allowing every MIDI event coming in to be also immediately sent back to another port. The port number is also defined as a preference and connected according to the output ports configuration.
Virtual Buses:
Your system may allow you to enable virtual MIDI buses (e.g. IAC buses on macOS). Virtual MIDI buses allow to abstract the device connection issues out from OM# (e.g. connect port 0 to IAC bus 1 and then set IAC bus 1 as the input of your synthesizer). Therefore devices and synthesizers can be connected and diconnected anytime to them, without needing to restart and reconfigure.
→ More info (and how to use this with Live)
Platform hints:
MacOS
→ MacOS has no embedded MIDI synth since QuickTime X / MacOS 10.6 (previous MacOS versions display “QuickTime GM Synth” in the default list of MIDI output devices).
→ Mac computers are shipped with GarageBand, which can be used to receive and render MIDI.
→ SimpleSynth is another free software synth compatible with MacOS ≤ 11, very easy to connect with OM#.Linux
→ Jack is a useful tool to connect MIDI and audio on Linux platforms.Windows
→ Windows distributions do generally contain an in-built MIDI synthesizer, visible by default in the MIDI devices list.